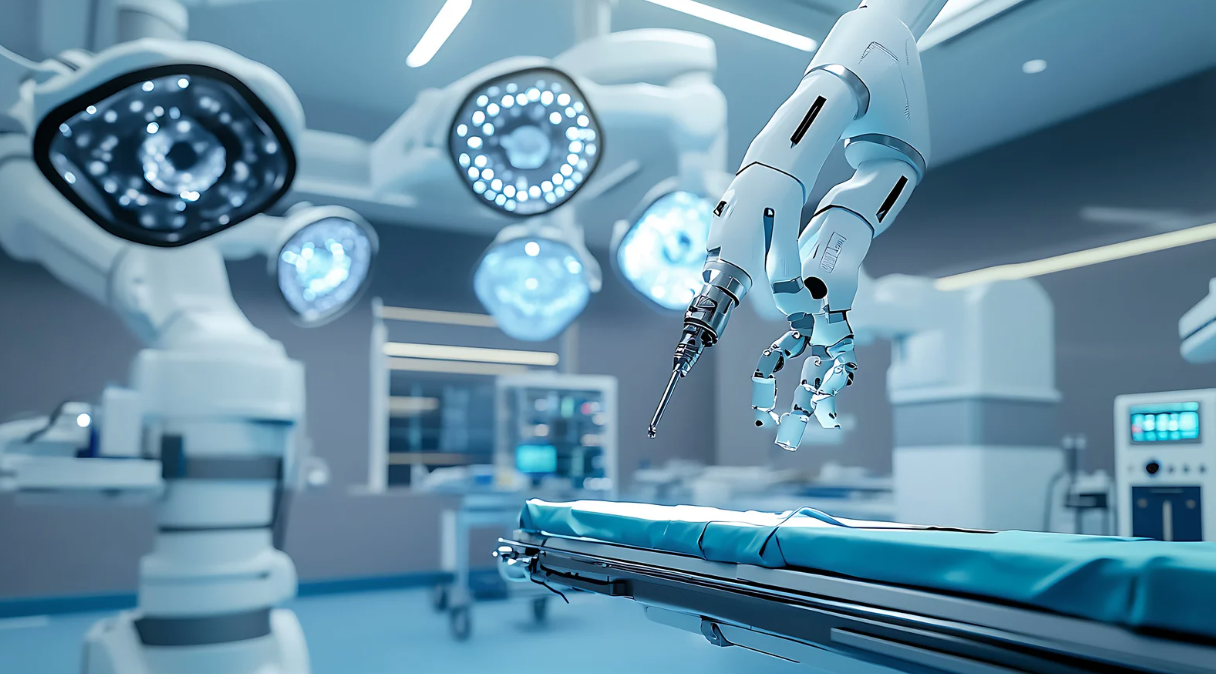
When you imagine robots, you might think of factory floors or science fiction movies. But the real revolution is happening somewhere far more human—inside hospitals. Robotics in healthcare is reshaping how doctors operate, how patients heal, and how medical facilities function every single day.
From surgical robots assisting in complex procedures to automated systems that deliver medicine across hospital corridors, robotics is redefining what productivity and precision mean in modern medicine. It’s not about replacing doctors—it’s about empowering them.
Let’s explore how robotics is driving automation and productivity across the healthcare industry, changing the way we approach care, efficiency, and recovery.
The Rise of Robotics in Healthcare
Technology and medicine have always shared a symbiotic relationship. From X-rays to telemedicine, innovation has consistently elevated patient outcomes and medical efficiency. Robotics, however, has taken this collaboration to an entirely new level.
In just the past decade, the adoption of robotics in healthcare has exploded. According to Allied Market Research, the global medical robotics market is expected to surpass $34 billion by 2030. This surge is fueled by one simple truth: robots make healthcare safer, faster, and more effective.
Modern healthcare robots don’t resemble the humanoid machines from films. Instead, they come in specialized forms—surgical assistants, rehabilitation aids, disinfection units, logistics carriers, and even companion robots. Each plays a unique role in transforming the care ecosystem.
How Robotics Is Automating Healthcare Processes
Hospitals are bustling environments where every second matters. Nurses race between rooms, surgeons perform delicate operations, and administrators juggle endless data. Robotics helps streamline all of this chaos into coordinated efficiency.
1. Surgical Robotics: Precision Beyond Human Hands
Imagine a surgeon performing a heart operation with hands that never tremble and eyes that magnify tissues a thousand times. That’s the promise of surgical robotics.
The most well-known example is the da Vinci Surgical System, which allows surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures using robotic arms controlled through a console. The robot translates a surgeon’s movements into ultra-precise actions inside the patient’s body.
The results? Smaller incisions, less blood loss, quicker recovery times, and reduced risk of infection. For hospitals, this translates into faster patient turnover and higher efficiency.
Surgical robots are also expanding into new specialties—orthopedics, neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and even dental procedures. These systems don’t replace surgeons; they amplify their capabilities.
2. Robotic Automation in Hospitals
Behind every successful surgery lies a mountain of administrative and logistical work. Robots are stepping in to handle these non-clinical but vital functions.
- Automated delivery robots transport medication, linens, and meals across hospital departments without human intervention.
- Robotic pharmacy systems accurately dispense prescriptions, minimizing medication errors.
- AI-driven scheduling robots optimize patient flow, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and waiting times are reduced.
For healthcare workers, this automation relieves them from repetitive tasks so they can focus on patient care—the heart of healthcare itself.
3. Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy Robots
After an injury or stroke, recovery often requires months of therapy and consistency. Robots are revolutionizing rehabilitation by providing personalized, measurable, and fatigue-free support.
Exoskeletons, for example, help patients regain mobility by guiding their movements with precision and tracking their progress in real time. These wearable robotics systems motivate patients while ensuring safety and consistency—something human therapists alone can’t always guarantee.
Notably, devices like Lokomat and ReWalk have already transformed rehabilitation centers, enabling thousands of patients to walk again after spinal cord injuries.
4. Disinfection and Sanitation Robots
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the use of UV disinfection robots, which autonomously sanitize hospital rooms, operating theaters, and public spaces.
By using ultraviolet light to kill pathogens, these robots dramatically reduce infection rates and minimize the exposure of healthcare workers to hazardous environments. Hospitals that deploy them report faster turnover times and safer working conditions—a perfect blend of productivity and safety.
5. Companion and Social Robots
Beyond automation, robotics in healthcare is also addressing an emotional need—companionship. Social robots like PARO, a therapeutic seal, and Pepper, a humanoid robot, offer comfort and engagement for elderly patients or those with dementia.
These robots help reduce loneliness, provide cognitive stimulation, and even monitor health parameters subtly. In long-term care facilities, they serve as tireless assistants, always ready to listen, remind, and comfort.
In an aging global population, such robots could play a key role in delivering empathetic, personalized care.
Boosting Productivity Across Healthcare Systems
Automation alone doesn’t define success—outcomes do. The beauty of robotics lies in its dual impact: improving patient care while optimizing hospital operations.
1. Faster Turnaround and Reduced Downtime
With surgical robots enabling shorter procedures and autonomous systems managing logistics, hospitals experience faster bed availability and improved scheduling. Every saved minute translates into higher throughput and better patient outcomes.
2. Reduced Human Error
In healthcare, even minor mistakes can have life-altering consequences. Robots minimize errors by following precise algorithms and maintaining consistent accuracy. Whether dispensing medication or assisting in surgery, robotic systems reduce variability—the enemy of quality.
3. Data-Driven Decision Making
Modern healthcare robots don’t just act—they learn. By collecting data from every interaction, they provide insights that enhance efficiency, predict bottlenecks, and personalize care plans.
Hospitals can now track everything from surgery duration to patient mobility metrics, enabling continuous improvement driven by real-world data.
4. Workforce Support and Burnout Reduction
Healthcare professionals are overworked and understaffed. Robotics automation helps redistribute the workload, reducing burnout and improving morale.
By handling menial tasks, robots give nurses and doctors time to connect with patients—a human touch technology can’t replace. The result is higher job satisfaction and better patient engagement.
Economic and Long-Term Benefits of Robotics in Healthcare
While the initial investment in robotics may seem steep, the long-term returns are undeniable.
- Cost Savings: Reduced errors, shorter hospital stays, and efficient resource allocation lower operational costs.
- Increased Patient Volume: Faster recovery and efficient scheduling enable hospitals to serve more patients effectively.
- Better Outcomes: Higher surgical precision means fewer complications and readmissions, saving both time and money.
- Sustainability: Robots optimize energy use, reduce waste, and improve supply chain efficiency, making healthcare more sustainable.
For governments and healthcare providers, robotics isn’t just an expense—it’s an investment in resilience and future readiness.
Challenges in Adopting Healthcare Robotics
Like any transformative technology, robotics in healthcare comes with challenges that must be addressed for sustainable growth.
- High Implementation Costs: Advanced surgical robots can cost millions, making them inaccessible for smaller hospitals.
- Training and Adaptation: Medical professionals require specialized training to operate and maintain robotic systems effectively.
- Ethical Concerns: Questions around patient privacy, data use, and human oversight continue to shape the robotics conversation.
- System Integration: Seamlessly connecting robots with existing hospital IT systems can be complex and time-consuming.
Despite these challenges, the trajectory is clear: as technology becomes more affordable and accessible, robotics will become a staple of modern medicine.
The Human-Robot Collaboration in Healthcare
Contrary to the common fear that robots might replace doctors, the future lies in collaboration, not competition.
Robots handle the precision, repetition, and data; humans provide empathy, creativity, and judgment. Together, they form a symbiotic partnership where each complements the other’s strengths.
Think of it as an orchestra: the robots are the instruments, perfectly tuned and tireless, while the doctors are the conductors, guiding every movement to create harmony.
This balance ensures that healthcare becomes not only more efficient but also more humane.
The Future of Robotics in Healthcare
The future of healthcare robotics promises even greater integration between humans and machines. Imagine AI-powered surgical assistants that anticipate a surgeon’s next move or nanorobots that deliver targeted drugs directly inside the body.
Emerging trends include:
- AI-Enhanced Diagnostics: Robots using deep learning to analyze medical images faster than radiologists.
- Remote Surgery: Surgeons operating across continents via robotic systems connected through 5G networks.
- Smart Prosthetics: Robotic limbs controlled by neural signals, offering natural movement and sensation.
- Homecare Robots: Assisting elderly or disabled patients with everyday tasks, ensuring independence and dignity.
The line between science and science fiction is blurring—and it’s transforming healthcare into a domain of precision, compassion, and innovation.
Conclusion
Robotics in healthcare is not just about machines taking over—it’s about redefining what’s possible. It’s about giving doctors superhuman precision, nurses more time to care, and patients faster recoveries.
Automation and productivity are no longer goals—they’re the foundation of a smarter, more responsive healthcare system. As robotics continues to advance, one thing becomes clear: the hospitals of tomorrow will not just be places of healing but hubs of innovation powered by intelligent machines and compassionate humans working side by side.
The future of healthcare is here—and it’s robotic.
FAQ
1. What are the main types of robotics in healthcare?
The main types include surgical robots, rehabilitation robots, hospital logistics robots, disinfection robots, and social companion robots.
2. How do surgical robots improve patient outcomes?
They enhance precision, reduce incision sizes, minimize blood loss, and lead to faster recovery times and shorter hospital stays.
3. Are robots replacing doctors and nurses?
No. Robots assist healthcare professionals by handling repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on complex care and patient interaction.
4. What are the biggest challenges of adopting robotics in healthcare?
High costs, training requirements, ethical concerns, and system integration are the main challenges faced by healthcare providers.
5. What does the future of robotics in healthcare look like?
Expect AI-driven robots capable of diagnostics, remote surgery, and personalized homecare, making healthcare more precise and accessible.