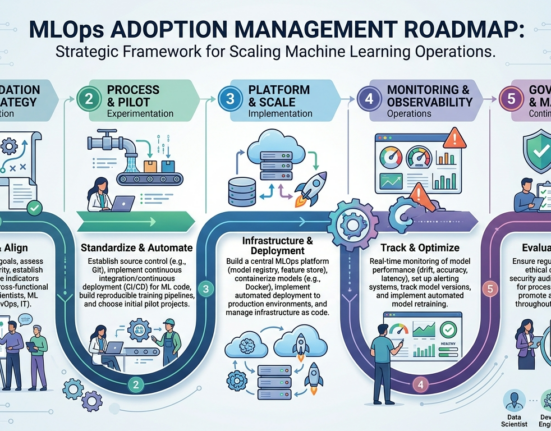
Robotics automation risk management sits at the heart of every successful automation initiative. From the first planning meeting to long-term operation, managing uncertainty determines whether a robotics project delivers value or creates disruption. Automation promises speed, precision, and efficiency, yet without structured risk awareness, those benefits can fade quickly.
Robotics projects combine machines, software, people, and processes. Each element introduces uncertainty. When risks are ignored, small issues turn into costly failures. When they are addressed early, automation becomes a powerful and dependable asset.
This article explores how to manage risks in robotics automation projects with clarity, balance, and foresight.
Why Risk Management Is Critical in Robotics Automation
Automation magnifies outcomes. When systems perform well, productivity scales rapidly. When failures occur, losses escalate just as fast.
Robotics automation risk management matters because these projects operate at the intersection of physical and digital systems. Hardware failures cause downtime. Software errors disrupt workflows. Human misunderstandings introduce safety concerns.
Without a clear approach to risk, teams rely on optimism. Optimism alone does not prevent budget overruns or safety incidents.
Effective risk management replaces assumptions with preparation. It supports innovation rather than slowing it.
Understanding Risk in Robotics Automation Projects
Risk does not always arrive dramatically. Often, it hides quietly in overlooked details.
A robot may struggle to integrate with legacy equipment. Operators may not receive enough training. Vendors may underestimate delivery timelines. Each issue feels manageable alone. Together, they derail progress.
Robotics automation risk management begins by expanding how teams define risk. It includes technical, operational, financial, and human factors.
Seeing risk clearly allows teams to respond intelligently.
Strategic Risks During Automation Planning
Many automation problems start before equipment arrives.
Unclear objectives create confusion later. Teams pursue robotics without defining success metrics. When goals remain vague, outcomes disappoint.
Another strategic risk involves automating the wrong process. Not every task benefits equally from robotics.
Encourages disciplined planning. Teams align automation goals with business priorities early.
Clear direction reduces downstream rework.
Technology Selection and Compatibility Risks
Choosing robotics technology shapes long-term outcomes.
Robots differ in payload, flexibility, and durability. Software platforms vary in openness and support. Vendor claims do not always reflect real-world performance.
Risk-aware teams validate assumptions through pilots and simulations.
Robotics automation risk management ensures technology serves operational needs, not marketing promises.
Careful selection prevents costly lock-in.
Integration Challenges in Existing Environments
Integration remains one of the most common failure points.
Robots rarely operate in isolation. They connect to conveyors, sensors, control systems, and enterprise software. Small mismatches create cascading delays.
Older infrastructure adds complexity. Interfaces behave unpredictably. Data flows break unexpectedly.
Robotics automation risk management identifies integration risks early. Teams allocate time for testing and adjustment.
Integration succeeds through realism, not speed.
Deployment Risks and Operational Disruption
Deployment turns planning into reality.
Installation can interrupt production. Unexpected downtime tests patience. New workflows confuse teams.
Operational risk increases when schedules are too aggressive. Rushed deployments amplify mistakes.
It favors phased rollouts. Gradual deployment allows learning without overwhelming staff.
Controlled implementation protects productivity and trust.
Safety Risks in Robotics Projects
Safety is never optional.
Robots move with force and precision. Without safeguards, accidents happen quickly. Even collaborative systems require careful design.
Safety risks include improper guarding, insufficient sensors, and unclear procedures.
Robotics automation risk management prioritizes safety assessments from the start. Layout, speed, and interaction rules follow risk analysis.
Training reinforces safe behavior.
Human Factors and Workforce Risks
Automation depends on people.
Resistance emerges when automation feels imposed. Fear of job loss fuels disengagement. Skill gaps cause misuse.
Robotics automation risk management addresses human concerns proactively. Communication, involvement, and training build trust.
When teams understand purpose, adoption improves.
Automation should support people, not sideline them.
Change Management as a Risk Control Tool
Change unsettles routines.
Automation alters roles and workflows. Without guidance, confusion grows.
Effective change management reduces resistance. Leaders explain goals clearly. Feedback channels stay open.
Robotics automation risk management treats change management as essential, not optional.
People adapt faster when included.
Project Governance and Coordination Risks
Robotics projects involve many stakeholders.
Poor coordination leads to missed dependencies and conflicting priorities. Scope creep strains budgets.
Robotics automation risk management strengthens governance. Clear roles, milestones, and communication paths reduce confusion.
Regular reviews surface issues early.
Structure supports flexibility.
Supplier and Vendor-Related Risks
Vendors influence success heavily.
Delays, quality issues, or limited support create risk. Dependence on one supplier increases exposure.
This includes vendor evaluation and contract clarity.
Strong partnerships reduce uncertainty.
Diversification improves resilience.
Financial Risks and Cost Control
Automation carries financial exposure.
Costs extend beyond equipment. Integration, training, maintenance, and downtime add up.
Underestimating total cost of ownership leads to disappointment.
Robotics automation risk management models realistic scenarios. Contingency planning absorbs surprises.
Financial discipline sustains confidence.
Schedule Pressure and Timeline Risks
Time pressure distorts decisions.
Compressed schedules reduce testing and training. Problems surface later, when fixes cost more.
Robotics automation risk management balances speed with readiness.
Realistic timelines reduce stress.
Early patience saves time overall.
Cybersecurity and Data Risks
Modern robots connect to networks.
Connectivity introduces cyber risk. Unauthorized access disrupts operations.
Robotics automation risk management includes cybersecurity planning. Access controls, monitoring, and updates protect systems.
Security extends beyond IT departments.
Operational resilience depends on protection.
Quality and Performance Uncertainty
Automation aims to improve quality.
Poor calibration or sensor drift undermines that goal. Software bugs affect output consistency.
Robotics automation risk management includes performance monitoring. Metrics track uptime, accuracy, and reliability.
Measurement guides correction.
Quality improves through vigilance.
Scalability and Expansion Risks
Success invites growth.
Scaling automation multiplies complexity. Solutions that work in one area may fail elsewhere.
Robotics automation risk management plans for scalability early. Modular designs reduce rework.
Standardization supports growth.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Automation operates within regulations.
Safety standards, labor rules, and industry requirements apply. Non-compliance carries penalties.
Robotics automation risk management integrates regulatory awareness early.
Compliance shapes design decisions.
Proactive alignment avoids rework.
Testing, Validation, and Edge Cases
Testing reveals reality.
Insufficient validation allows hidden flaws into production. Rare scenarios trigger failures.
Robotics automation risk management emphasizes robust testing. Simulations complement physical trials.
Edge cases deserve attention.
Confidence grows through verification.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Planning
Robots require care.
Maintenance lapses reduce reliability. Spare parts availability matters.
Robotics automation risk management plans for lifecycle support. Schedules, documentation, and training protect uptime.
Longevity depends on preparation.
Knowledge Transfer and Dependency Risks
Knowledge silos weaken systems.
If only a few experts understand automation, absence creates disruption.
Robotics automation risk management promotes documentation and cross-training.
Shared knowledge builds resilience.
Dependency creates fragility.
Risk Assessment Tools and Methods
Structured tools support decisions.
Risk matrices, failure analysis, and simulations provide clarity.
Robotics automation risk management benefits from formal frameworks.
Tools support judgment, not replace it.
Consistency improves outcomes.
Monitoring Risk After Go-Live
Risk continues after launch.
Usage patterns evolve. Wear increases. Context changes.
Robotics automation risk management includes ongoing monitoring.
Alerts and audits identify emerging issues.
Vigilance sustains performance.
Balancing Innovation and Risk Awareness
Excess caution stalls progress.
Too little caution invites failure.
Robotics automation risk management finds balance. Safe experimentation supports learning.
Pilot environments enable innovation.
Boundaries protect creativity.
Leadership and Risk Culture
Leadership sets tone.
When leaders value preparation, teams follow.
Robotics automation risk management requires visible commitment.
Support empowers teams.
Culture shapes behavior.
Learning From Automation Failures
Failure teaches lessons.
Post-project reviews reveal patterns. Assumptions get challenged.
Robotics automation risk management includes learning loops.
Reflection builds maturity.
Mistakes become assets.
The Future of Risk Management in Robotics
Automation grows smarter.
AI-driven robots adapt in real time. Risk profiles shift.
Future approaches will predict issues before failure occurs.
Preparation replaces reaction.
The future rewards readiness.
Conclusion
Managing risks in robotics automation projects is not about limiting ambition. It is about protecting it. Robotics automation risk management transforms uncertainty into structured preparation, helping teams deliver safe, scalable, and reliable automation solutions.
By addressing technical, human, financial, and operational risks together, organizations build confidence and resilience. Automation then delivers lasting value rather than short-term gains.
Successful robotics projects are not risk-free. They are risk-aware. That awareness makes all the difference.
FAQ
1. What does robotics automation risk management involve?
It involves identifying, assessing, and reducing risks across planning, deployment, and operation.
2. Why do automation projects commonly fail?
Failures often result from poor planning, integration issues, and underestimated human factors.
3. How can safety risks be reduced in robotics projects?
Through risk assessments, proper guarding, training, and compliance with safety standards.
4. Should risk management continue after deployment?
Yes. Ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential as conditions change.
5. Does risk management slow down automation innovation?
No. It enables innovation by preventing costly failures and building long-term confidence.