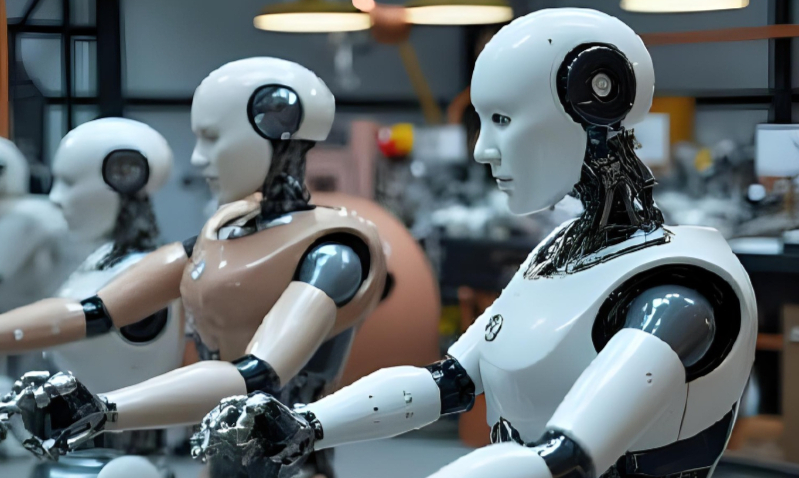
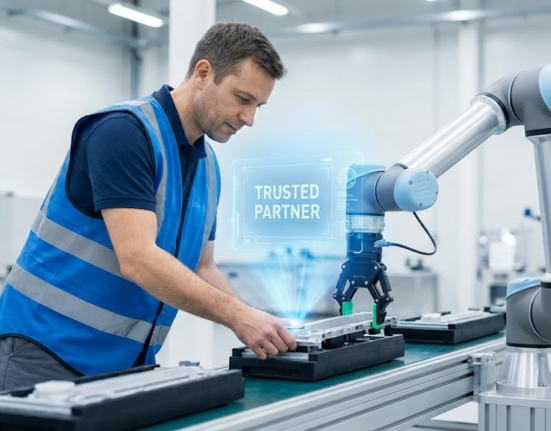
Collaborative robotics—often called cobots—is redefining what it means to work in the age of automation. Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate separately from humans, cobots are designed to work side by side with people, combining the precision of machines with the creativity and problem-solving skills of humans.
As automation continues to expand, understanding how collaborative robotics will shape the future workforce is essential for both businesses and employees who want to thrive in a technology-driven world.
What Are Collaborative Robots (Cobots)?
Collaborative robots are intelligent machines designed to safely interact and cooperate with humans in shared workspaces. Equipped with sensors, vision systems, and adaptive learning, cobots can adjust to real-time changes, making them ideal partners for human workers rather than replacements.
They differ from traditional robots in three key ways:
- Safety: Cobots can detect human presence and reduce speed or stop when needed.
- Flexibility: They can be easily reprogrammed for new tasks.
- Collaboration: Cobots assist humans, complementing rather than replacing their skills.
Why Collaborative Robotics Is the Future
As industries evolve, companies are recognizing that combining human intelligence with robotic efficiency creates the best results. The global cobot market is projected to exceed $10 billion by 2030, driven by demand for flexible automation, worker safety, and productivity.
Cobots represent not a replacement for people—but an evolution of work itself.
The Human-Robot Partnership
Collaborative robotics doesn’t eliminate jobs; it transforms them. Humans handle creativity, judgment, and problem-solving, while robots manage repetitive, dangerous, or precision-based tasks. Together, they form a hybrid workforce that maximizes both efficiency and innovation.
This partnership allows employees to focus on higher-value work such as strategy, maintenance, or product improvement—areas where human insight remains unmatched.
Alt text: collaborative robotics future workforce with humans and cobots working together
Key Industries Adopting Collaborative Robotics
1. Manufacturing
Cobots assist in assembly, welding, packaging, and inspection tasks, increasing productivity while improving worker safety.
2. Healthcare
Cobots help surgeons with precision operations, handle lab samples, and support rehabilitation therapy for patients.
3. Logistics and Warehousing
In warehouses, cobots transport goods, manage inventory, and work alongside staff to fulfill orders faster and with fewer errors.
4. Retail and Hospitality
Cobots assist with shelf stocking, cleaning, and customer service—freeing human workers to focus on experience and engagement.
5. Agriculture
Collaborative robots perform planting, harvesting, and monitoring tasks, helping farmers overcome labor shortages and improve yields.
Benefits of Collaborative Robotics for the Workforce
1. Enhanced Productivity
Cobots reduce manual strain and perform repetitive tasks efficiently, allowing workers to focus on creative, technical, and supervisory roles.
2. Improved Workplace Safety
Cobots take on hazardous jobs such as heavy lifting or exposure to toxic environments, minimizing workplace injuries.
3. Skill Development and Reskilling
As cobots become common, workers gain new opportunities to learn programming, data analysis, and maintenance—skills that increase career value.
4. Greater Job Satisfaction
Employees feel more fulfilled when freed from monotonous tasks. Collaboration with intelligent machines encourages innovation and engagement.
Alt text: collaborative robotics improving productivity and worker safety in manufacturing
How Collaborative Robotics Is Changing Job Roles
Collaborative robotics doesn’t eliminate human labor—it changes what labor looks like. Roles are shifting from manual execution to digital oversight, such as:
- Robot Operators and Technicians: Manage and maintain cobots.
- Data Analysts: Interpret robotic performance data to optimize workflows.
- Automation Engineers: Design systems where cobots and humans interact seamlessly.
- Safety Supervisors: Ensure compliance with collaborative robot safety standards.
The workforce of the future will be defined not by competition between humans and robots—but by cooperation.
Reskilling for a Collaborative Future
To thrive in the cobot era, workers must adapt through continuous learning and reskilling. Essential skills include:
- Programming and Robotics Control: Basic coding and system configuration.
- Problem-Solving: Adapting to new processes as technology evolves.
- Communication and Collaboration: Coordinating effectively with both humans and machines.
- Data Literacy: Understanding and using robotic performance insights.
Businesses must invest in reskilling initiatives to ensure employees are equipped for hybrid human-machine teams.
Small Businesses and Collaborative Robotics
Cobots are no longer exclusive to large corporations. Their affordability and flexibility make them ideal for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). They can handle production spikes, adapt to changing product lines, and reduce labor shortages—all without replacing workers.
This democratization of robotics means innovation is no longer limited to big factories; even small workshops can benefit from automation.
Ethical and Social Considerations
As collaborative robotics reshapes the workforce, ethical challenges must be addressed.
- Transparency: Workers should understand how decisions are made in robot-human teams.
- Equity: Ensure that automation benefits all employees, not just a few.
- Job Security: Communicate clearly that cobots are designed to assist, not replace.
Responsible adoption builds trust and ensures sustainable technological growth.
Challenges in Implementing Collaborative Robotics
Adopting cobots isn’t without obstacles. Common challenges include:
- High initial setup costs.
- Lack of skilled workers for programming and maintenance.
- Integration with existing workflows and safety standards.
However, as technology becomes more user-friendly and affordable, these barriers are rapidly diminishing.
Future Trends in Collaborative Robotics
Looking ahead, several innovations will shape how cobots integrate into the workforce:
- AI-Powered Adaptation: Cobots that learn tasks autonomously through observation.
- Cloud Robotics: Shared intelligence across connected robots.
- Soft Robotics: Cobots with flexible designs that mimic human touch.
- Human-Aware Safety Systems: Predictive sensors that ensure seamless cooperation.
These trends will make cobots smarter, safer, and even more human-centric.
Conclusion: Building a Collaborative Future
Collaborative robotics is not the end of human work—it’s the next evolution of it. By merging machine precision with human creativity, we’re entering an era where technology empowers rather than replaces people.
Companies that embrace this partnership will see greater innovation, safety, and productivity. Workers who reskill and adapt will find new opportunities in the world of human-robot collaboration.
The future workforce won’t be human or robotic—it will be collaborative.
FAQ
1. What are collaborative robots?
They are robots designed to safely work alongside humans, assisting with tasks rather than replacing workers.
2. How will collaborative robotics impact jobs?
Cobots will transform roles, emphasizing creativity, strategy, and technical skills over repetitive labor.
3. What industries use collaborative robotics most?
Manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, and retail are leading adopters.
4. Do workers need new skills to work with cobots?
Yes, employees should develop programming, data analysis, and collaboration skills.
5. What’s the long-term future of collaborative robotics?
Expect workplaces where humans and cobots collaborate seamlessly to achieve higher efficiency, safety, and innovation.