The healthcare industry is undergoing a digital revolution. Among the many innovations transforming modern medicine, computer vision stands out as a true game-changer. By enabling machines to “see” and interpret medical images, this technology is helping doctors diagnose diseases earlier, assist surgeries with precision, and improve patient care outcomes across the board. But how exactly does computer vision in healthcare make such a difference—and where is it headed next?
Let’s dive into how this fascinating technology is redefining medical efficiency, accuracy, and compassion in patient care.
Understanding Computer Vision in Healthcare
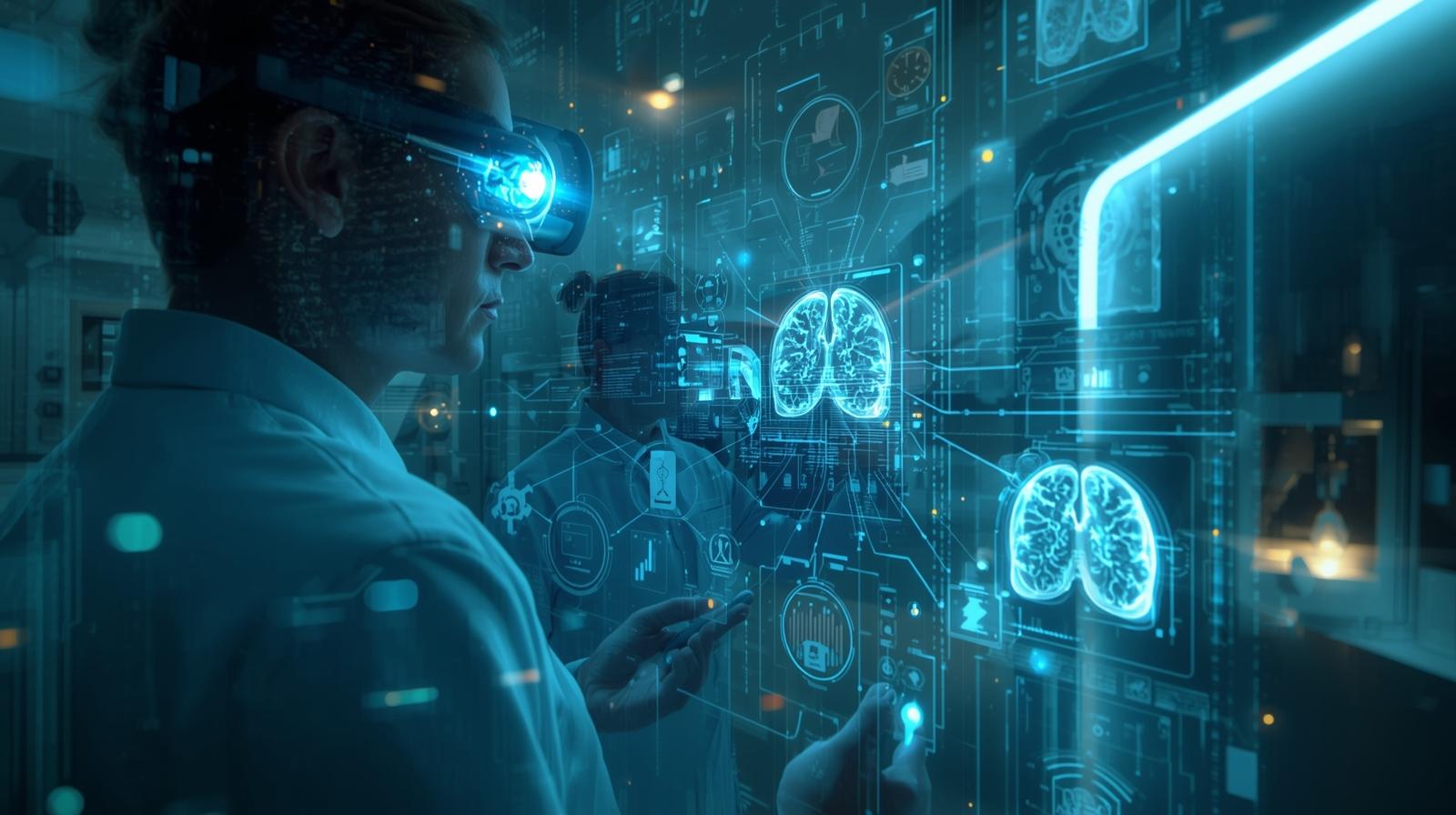
Computer vision refers to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows computers to interpret visual data from the world—just like humans do. In healthcare, this means enabling machines to analyze medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and even live video feeds from surgical procedures.
Unlike traditional imaging methods that rely solely on human interpretation, computer vision can process vast amounts of visual data quickly and with exceptional precision. This doesn’t replace human expertise; rather, it augments it. Doctors gain an extra layer of analysis that helps them detect patterns invisible to the naked eye.
The Role of Computer Vision in Modern Diagnostics
Early and accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective patient care. Computer vision dramatically enhances this process. For instance, AI models trained on millions of medical images can identify abnormalities—such as tumors, fractures, or blood clots—within seconds.
Hospitals are increasingly using this technology to assist radiologists. A deep-learning model can scan through thousands of X-rays faster than a human team could, flagging potential problem areas for review. As a result, patients receive quicker feedback, and doctors can focus more on treatment instead of data analysis.
Additionally, computer vision systems can help detect diseases like diabetic retinopathy, pneumonia, or breast cancer at stages far earlier than traditional screenings often allow. Early detection means earlier intervention—and ultimately, higher survival rates and better outcomes.
Enhancing Surgical Precision through Computer Vision
Imagine a surgeon operating with AI-assisted vision. That’s no longer science fiction. Computer vision-powered systems are now being integrated into operating rooms to assist with precision-guided surgery.
Using real-time imaging and AI analytics, these systems help surgeons navigate delicate procedures with pinpoint accuracy. For example, during minimally invasive surgeries, computer vision algorithms can track instruments, identify anatomical structures, and warn surgeons of potential hazards.
This level of guidance reduces human error, minimizes tissue damage, and shortens recovery time. In orthopedic and neurosurgical operations, robotic systems paired with computer vision provide unparalleled control, offering consistency that complements human expertise.
The outcome? Safer surgeries, quicker healing, and greater patient confidence.
Improving Patient Monitoring and Safety
Beyond diagnostics and surgery, computer vision in healthcare is revolutionizing patient monitoring. AI-powered cameras in hospitals can detect patient movement patterns, ensuring safety and comfort.
For instance, systems can alert nurses when a patient attempts to leave bed unassisted, reducing fall risks—especially in elderly care units. They can also monitor vital signs such as breathing rate, skin color, or facial expressions to detect discomfort or distress without invasive equipment.
In intensive care units (ICUs), this technology adds another layer of protection. Real-time visual analytics help medical staff react quickly to emergencies, monitor staff hygiene compliance, and ensure procedural accuracy.
Streamlining Administrative and Workflow Efficiency
Not all benefits of computer vision are clinical. Administrative burdens are among the most time-consuming aspects of healthcare. Fortunately, computer vision can automate many of these tasks.
From digitizing handwritten medical forms to analyzing patient flow in hospitals, AI vision tools streamline operations. Cameras can monitor waiting rooms to optimize staffing, while automated systems verify patient identity, track medication dispensing, and ensure compliance with protocols.
This level of automation doesn’t just cut costs—it frees up healthcare professionals to focus more on what truly matters: patient care.
Supporting Remote and Telemedicine Solutions
Telemedicine has become essential in today’s world. Computer vision enhances virtual healthcare by bringing clinical-grade accuracy to remote environments.
Patients can now use smartphone cameras to send images or videos of symptoms, such as skin rashes or wounds, to their doctors. Computer vision algorithms analyze these visuals, offering real-time insights and recommendations before a professional consultation.
In remote areas where specialists are scarce, this capability bridges critical gaps in access. With AI assistance, local clinics can provide expert-level assessments, reducing travel and treatment delays.
Reducing Human Error in Diagnosis
Even the best medical professionals are human—and humans can make mistakes. Fatigue, bias, or sheer information overload can lead to misdiagnoses. Computer vision helps mitigate these risks by providing consistent, unbiased analysis.
By comparing medical scans against vast datasets, the system identifies subtle patterns that even experienced radiologists might overlook. When used as a decision-support tool, computer vision increases diagnostic accuracy and reinforces clinical confidence.
In fields such as oncology, cardiology, and dermatology, AI-powered image interpretation is already achieving accuracy rates that rival or exceed human experts.
Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Of course, with great technological power comes great responsibility. Integrating computer vision into healthcare raises valid concerns about data privacy, bias, and transparency.
Patient images are sensitive information that must be handled with care. Healthcare providers using AI tools must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR to ensure data protection. Moreover, developers must train algorithms on diverse datasets to prevent bias in diagnosis or treatment recommendations.
Transparency is equally important. Patients should be informed about how AI tools are used in their care and how their data contributes to improving medical models. When used responsibly, computer vision can strengthen trust between patients and providers, not undermine it.
The Future of Computer Vision in Patient Care
Looking ahead, computer vision in healthcare will only grow more sophisticated. Emerging technologies such as 3D imaging, augmented reality (AR), and wearable sensors will further expand its applications.
Imagine smart glasses that help doctors visualize a patient’s anatomy during procedures, or wearable devices that continuously analyze skin changes to detect early signs of disease. Combined with robotics and machine learning, these advancements could transform hospitals into intelligent ecosystems that anticipate patient needs before symptoms even appear.
As algorithms become more explainable and data integration improves, computer vision will shift from a supportive tool to an essential component of personalized medicine.
Challenges to Overcome Before Full Integration
Despite its promise, challenges remain. Implementing computer vision in healthcare requires extensive data, robust infrastructure, and regulatory approval.
Some healthcare systems still lack the digital readiness to adopt such advanced tools. Integration also requires training medical professionals to interpret and trust AI-driven insights.
Moreover, balancing automation with human empathy is crucial. Technology should enhance, not replace, the compassion that defines quality patient care. As hospitals navigate these hurdles, partnerships between AI developers, clinicians, and policymakers will be key to unlocking the full potential of computer vision.
Conclusion
Computer vision in healthcare is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a present-day revolution shaping the future of medicine. By merging the analytical power of machines with the empathy and expertise of medical professionals, this technology enhances diagnostics, surgery, monitoring, and overall patient care.
While challenges like data privacy and ethical concerns remain, the direction is clear: healthcare will become faster, smarter, and more human-centered with computer vision as its guiding lens. As innovation continues, every image, scan, and visual signal brings us one step closer to truly personalized and proactive patient care.
FAQ
1. How does computer vision improve patient diagnosis?
Computer vision analyzes medical images faster and more accurately, helping doctors detect diseases early and reduce diagnostic errors.
2. What are examples of computer vision in healthcare?
Examples include AI-assisted radiology, surgical navigation systems, patient monitoring cameras, and telemedicine diagnostic tools.
3. Can computer vision replace doctors?
No. Computer vision supports doctors by providing insights and automation, but human expertise remains essential for decision-making and patient interaction.
4. Is computer vision safe for patient data?
When used properly under regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, computer vision systems are designed to protect patient privacy and secure sensitive data.
5. What’s the future of computer vision in healthcare?
The future involves integrating computer vision with AR, robotics, and personalized medicine to create smarter, safer, and more responsive healthcare systems.